What is Yoga?
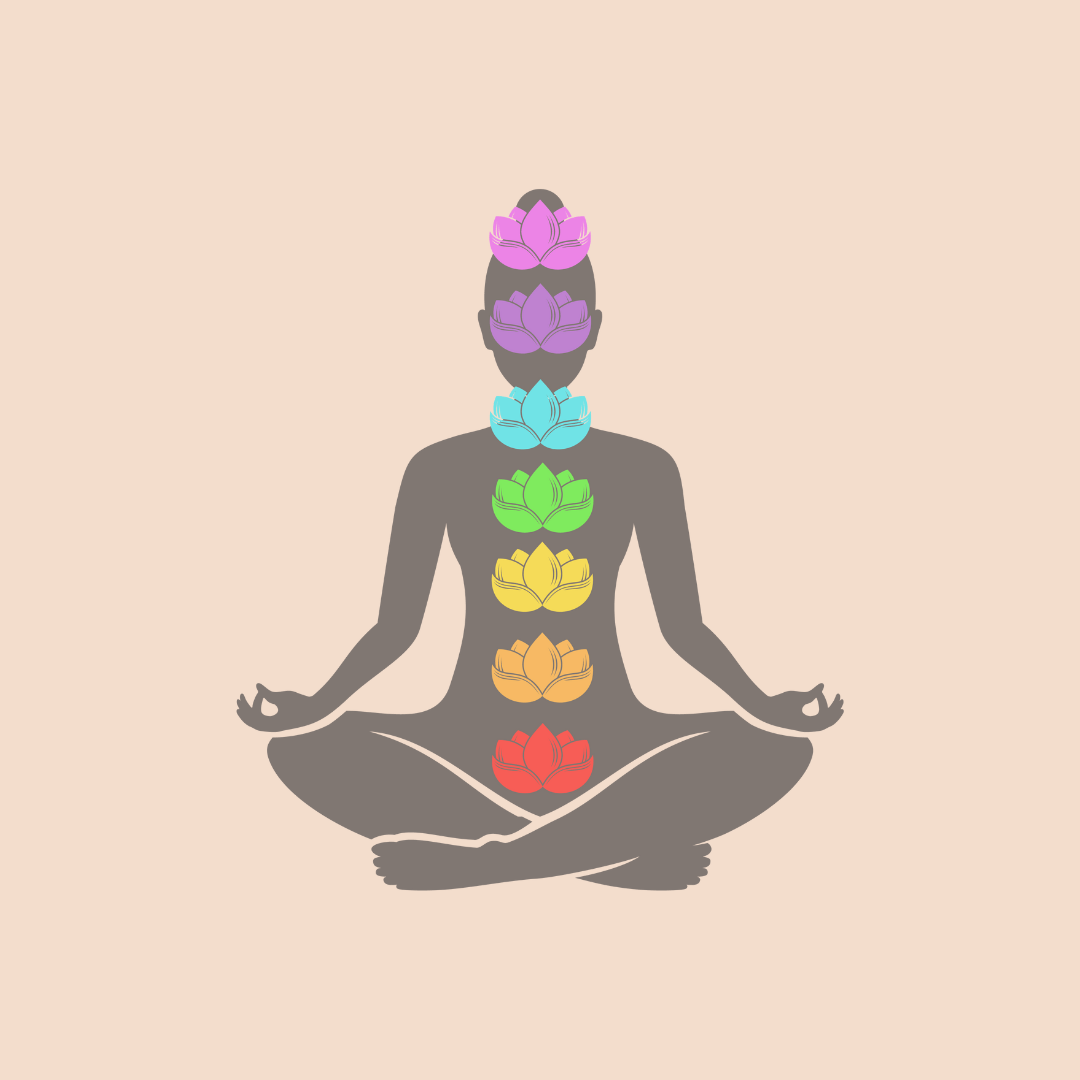
Historical Roots:
Yoga finds its roots in ancient Indian philosophy and spirituality. The earliest mention of yoga dates back to the Vedas, ancient texts that form the basis of Hindu scriptures. The foundational text of yoga philosophy is the Yoga Sutras, compiled by the sage Patanjali around 2,000 years ago. This text outlines the principles and practices of yoga, providing a roadmap for spiritual growth and self-realization.
The Eight Limbs of Yoga:
Patanjali's Yoga Sutras introduce the Eight Limbs of Yoga, a systematic guide to living a meaningful and purposeful life. These limbs are:
Yamas (Ethical Principles): The social and ethical guidelines encompassing non-violence, truthfulness, non-stealing, celibacy, and non-attachment.
Niyamas (Personal Disciplines): Individual observances involving purity, contentment, self-discipline, self-study, and surrender to a higher power.
Asanas (Physical Postures): The familiar aspect of yoga involving physical poses designed to promote strength, flexibility, and balance.
Pranayama (Breath Control): Techniques to regulate and control the breath, linking it to the mind and enhancing vitality.
Pratyahara (Withdrawal of Senses): Turning attention inward by detaching from external stimuli, promoting introspection.
Dharana (Concentration): Focusing the mind on a single point, fostering mental clarity.
Dhyana (Meditation): The practice of sustained focus, leading to a state of deep concentration.
Samadhi (Union): The ultimate goal of yoga, where the practitioner experiences a profound connection with the divine or universal consciousness.
Physical and Mental Benefits:
While the philosophical aspects of yoga provide a spiritual framework, the physical practice of asanas offers numerous health benefits. Regular yoga practice can enhance flexibility, strength, and balance. It also promotes relaxation and stress reduction through the integration of breath and movement.
Various Styles of Yoga:
Yoga is not a one-size-fits-all practice. There are numerous styles catering to different needs and preferences. Some popular styles include:
- Hatha Yoga: A foundational practice that emphasizes physical postures and basic breath control.
- Vinyasa Yoga: Characterized by flowing sequences of poses coordinated with breath, promoting a dynamic and fluid practice.
- Iyengar Yoga: Focuses on precision and alignment in poses, often using props to assist in achieving correct form.
- Ashtanga Yoga: A dynamic and physically demanding practice involving a set sequence of poses, promoting strength and endurance.
- Kundalini Yoga: Combines postures, breath work, and chanting to awaken and activate spiritual energy.
Mind-Body Connection:
Yoga emphasizes the interconnectedness of the mind and body. The practice encourages self-awareness, mindfulness, and the cultivation of a calm and focused mind. Through the integration of physical postures, breath control, and meditation, practitioners aim to achieve a state of balance, well-being, and spiritual awakening.
In essence, yoga is a holistic and transformative journey, offering a path to self-discovery, inner peace, and a harmonious connection with the world. It's a timeless practice that continues to evolve, adapting to the needs and aspirations of those who embark on this profound exploration of the self. Embrace the essence of yoga and make your yoga, what you want it to be. Our journey has taken us to unexpected places—physically, mentally, and spiritually. It has been a guide, a challenge, and a source of joy. Our yoga mats are not just products; they are an extension of this journey, inviting others to step onto the path of self-discovery and well-being.
Love,
Laura



Comments